Introduction to Anote PrivateGPT
Anote PrivateGPT enables enterprises to leverage generative AI and privacy preserving LLMs to chat with your documents while keeping your private and data secure. Anote's Private GPT provides enterprises with their own AI assistant, acting as a chief artificial intelligence officer for a specific organization. Members of the organization are able to ask any question about the organization, and private GPT can answer any query based on your organizations data, while keeping the data local, on premise, private and secure. Members of the organization can chat with their documents to obtain relevant insights, and are shown citations of where the answers specifically come from within documents in their enterprise. For enterprises, this can be viewed as an on premise GPT-for-your-business, where enterprises have their own GPT, catered specifically for their needs. At the same time, enterprises have no risk of sharing confidential and private data, as data is kept on premise, local, private and secure.
Key Features
- Local Environment: Anote PrivateGPT operates entirely within the user's local environment, providing a secure and private space for document interactions.
- Document Storage: User documents are stored locally in a Chroma vector store, ensuring that they remain securely stored on the user's device or local storage infrastructure.
- Privacy-Preserving Retrieval: Anote incorporates a privacy-preserving retrieval component that efficiently searches and retrieves relevant documents based on user queries. The retrieval process takes place locally, without transmitting sensitive information to external servers.
- Privacy-Aware Language Models: Anote employs privacy-aware language models like LlamaCpp and GPT4All, which operate locally on the user's device or local infrastructure. These models preserve user privacy by avoiding the transmission of user queries or documents to external servers.
- Query-Response Privacy: Anote ensures that user queries and responses are kept private. User queries are processed locally, and the system only reveals relevant answers without disclosing the underlying content or details of the user's documents.
- Secure Execution: Anote implements security measures to protect the integrity and confidentiality of user data during execution. This includes secure execution environments, encryption of sensitive data, secure APIs and interfaces, and adherence to best practices for securing local infrastructure.
- User Control and Consent: Anote prioritizes user control and consent. Users have full control over their documents and data, including the ability to choose which documents to include, initiate queries, and receive answers. Interactions with the system are based on explicit user consent and preferences.
By combining these principles, Anote PrivateGPT empowers users to chat with their documents in a privacy-preserving way using the capabilities of the generative AI models. The focus on local execution, document storage, privacy-aware models, secure infrastructure, and user control ensures that your data remains confidential, secure and on premise.
How Does Anote PrivateGPT Works?
At Anote, you can easily upload your documents in various formats, including pdf, email, html, docx, and csv. After uploading, you can initiate a chat session in our user-friendly interface to interact with your uploaded documents. You can type in your prompts, and our system will provide you with accurate and relevant responses based on analyzing the documents. Our user interface not only presents answers to your main prompts but also includes references to the specific sections in the source documents where the information was found. By clicking on the eye button, you can easily navigate to the relevant document chunks and view the exact location of the retrieved information.
Large Language Model and Our Backend
The previous sections show how Anote PrivateGPT would work from user perspective. The flow chart below illustrates how Anote PrivateGPT works in the backend. In general, we utilize two important pipelines: data ingestion and query processing.
Data ingestion involves downloading user input documents, dividing them into chunks, and securely storing the embeddings of the chunks in a local vector database using Chroma. Anote PrivateGPT supports various formats, including .csv, .doc, .docx, .enex, .eml, .epub, .html, .md, .odt, .pdf, .ppt, .pptx, and .txt.
The query processing pipeline involves processing user queries and leveraging the local Chroma vector database to retrieve relevant document chunks. The retrieval process is followed by answer generation using powerful language models like LlamaCpp and GPT4All.
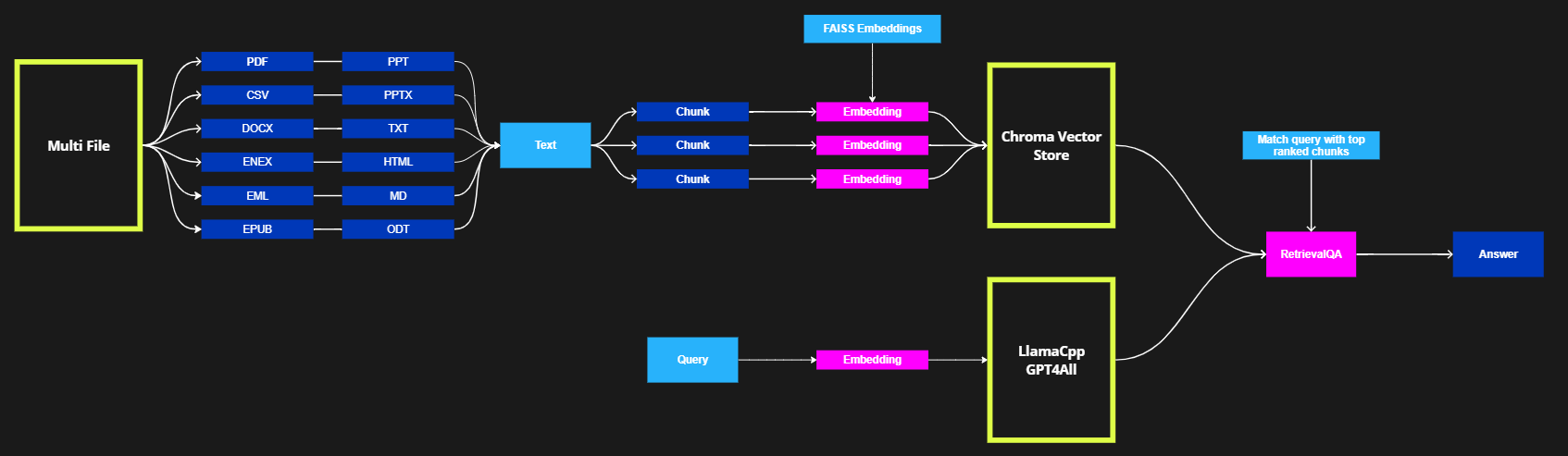
The step-by-step process involved in Anote PrivateGPT's pipeline is as follows:
def main():
# Parse the command line arguments
args = parse_arguments()
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name=embeddings_model_name)
db = Chroma(
persist_directory=persist_directory,
embedding_function=embeddings,
client_settings=CHROMA_SETTINGS
)
retriever = db.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": target_source_chunks})
# activate/deactivate the streaming StdOut callback for LLMs
callbacks = [] if args.mute_stream else [StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()]
# Prepare the LLM
match model_type:
case "LlamaCpp":
llm = LlamaCpp(
model_path=model_path,
n_ctx=model_n_ctx,
n_batch=model_n_batch,
callbacks=callbacks,
verbose=False
)
case "GPT4All":
llm = GPT4All(
model=model_path,
n_ctx=model_n_ctx,
backend='gptj',
n_batch=model_n_batch,
callbacks=callbacks,
verbose=False
)
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=retriever,
return_source_documents=not args.hide_source
)
- Embeddings Initialization: An instance of the HuggingFaceEmbeddings class is initialized to generate embedding vectors for the documents and capture their semantic representations.
- Vector Store Creation: An instance of the Chroma class is created to represent the vector store where document embeddings are securely stored. Chroma provides efficient retrieval capabilities for subsequent steps.
- Retrieval Setup: The code calls the
as_retriever()method on the Chroma vector store object (db). This method creates and returns a retriever object. Additional arguments can be provided using thesearch_kwargsparameter. In this case,{"k": target_source_chunks}specifies the number of top-ranked documents to retrieve. The value oftarget_source_chunksdetermines the desired number of retrieved documents. - Language Model Selection: The code checks the
model_typeto determine the appropriate language model (LLM) for answering the questions. Depending on themodel_type, either an instance of LlamaCpp or GPT4All is created. These LLMs are distinct implementations of language models that will be utilized to generate answers based on the retrieved documents. - RetrievalQA Instance: Finally, an instance of the RetrievalQA class is created, combining the retriever object, the selected LLM instance, and other necessary parameters. This class orchestrates the question-answering process, leveraging the retriever's retrieved documents and the LLM's language understanding and generation capabilities.
