Semi Structured Prompting
Semi-structured prompting refers to a method of querying or instructing a language model where the input includes both structured and unstructured elements. The structured prompts are typically categorical, directing the AI towards specific classes or categories of responses. An example of a structured prompt could be asking the customer to rate their satisfaction on a numeric scale from 1 to 5 (structured, categorical output).
The unstructured prompts, on the other hand, are typically freeform, allowing a broader scope for the AI's responses. An example of an unstructured prompt could be requesting the customer to provide a written explanation for their rating (unstructured, free-form text output).
Semi strucutured prompting encapsulates a wide variety of prompt types, including entity citations, chained prompts, or taxonomy-based tagging or classification or information extraction from text.
Here are examples for each type of prompt mentioned:
Entity Citations - This could involve prompting the AI to pull out specific information from a given resource. For instance, "Using the provided URL, list the names of all presidents from the 18th century, in format url | president_name"
Chained Prompts - This involves a sequence of prompts that build upon each other. For example, a first prompt might be "Describe the key events of World War II", followed by "Who were the major players involved in these events?" and "What were the global implications of these events?"
Information Extraction - Here, the AI might be asked to identify and extract specific entities or information from a block of text. An example could be, "Identify and list all the names of people mentioned in the following news article."
Multi-label Tagging/Classification - In this case, the AI would be prompted to categorize the input data based on a predefined taxonomy. For example, "Classify the following list of animals into the categories: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish."
This combination of structured and unstructured prompting makes semi-structured prompting a versatile tool for interacting with AI systems. Semi-Structured Prompting is very helpful in the financial domain, for fine tuning models to provide more accurate results in relation to earnings call transcripts.
As seen, semi-structured prompting with active learning can be used to answer many questions on financial documents such as earnings call transcripts. It can also be very helpful for other financial documents, such as Annual Reports, 10-Qs or 10-Ks. Below, we will go through an example of leveraging active learning to improve the answers from 10-K documents with human feedback.
Example: Information Extraction for 10-Ks
Extracting information from long documents, such as 10-K reports, can be a time-consuming and challenging task. One approach to simplify the process is by leveraging the power of language models like ChatGPT, Claude, BARD or other Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate summaries based on given prompts.
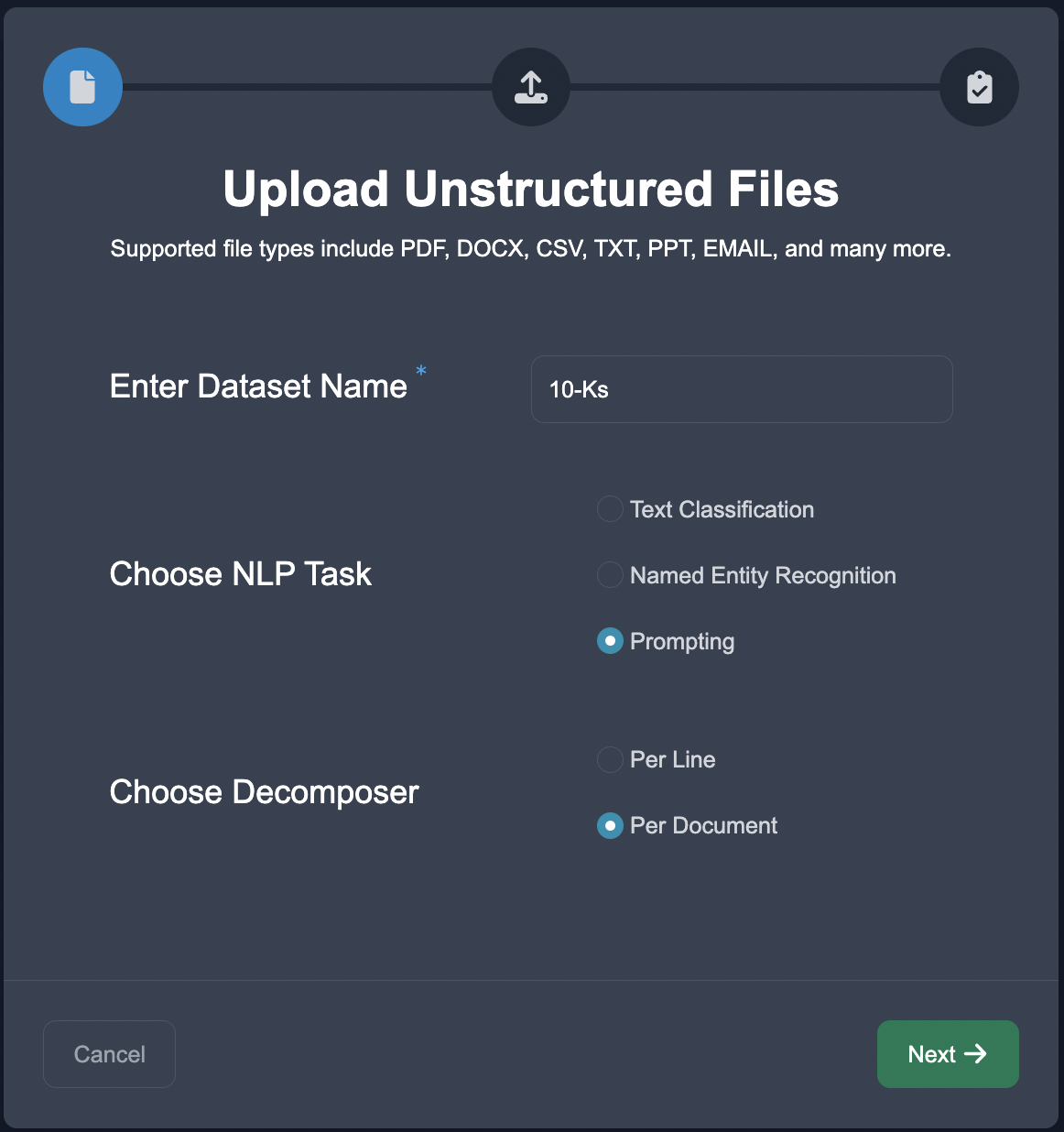
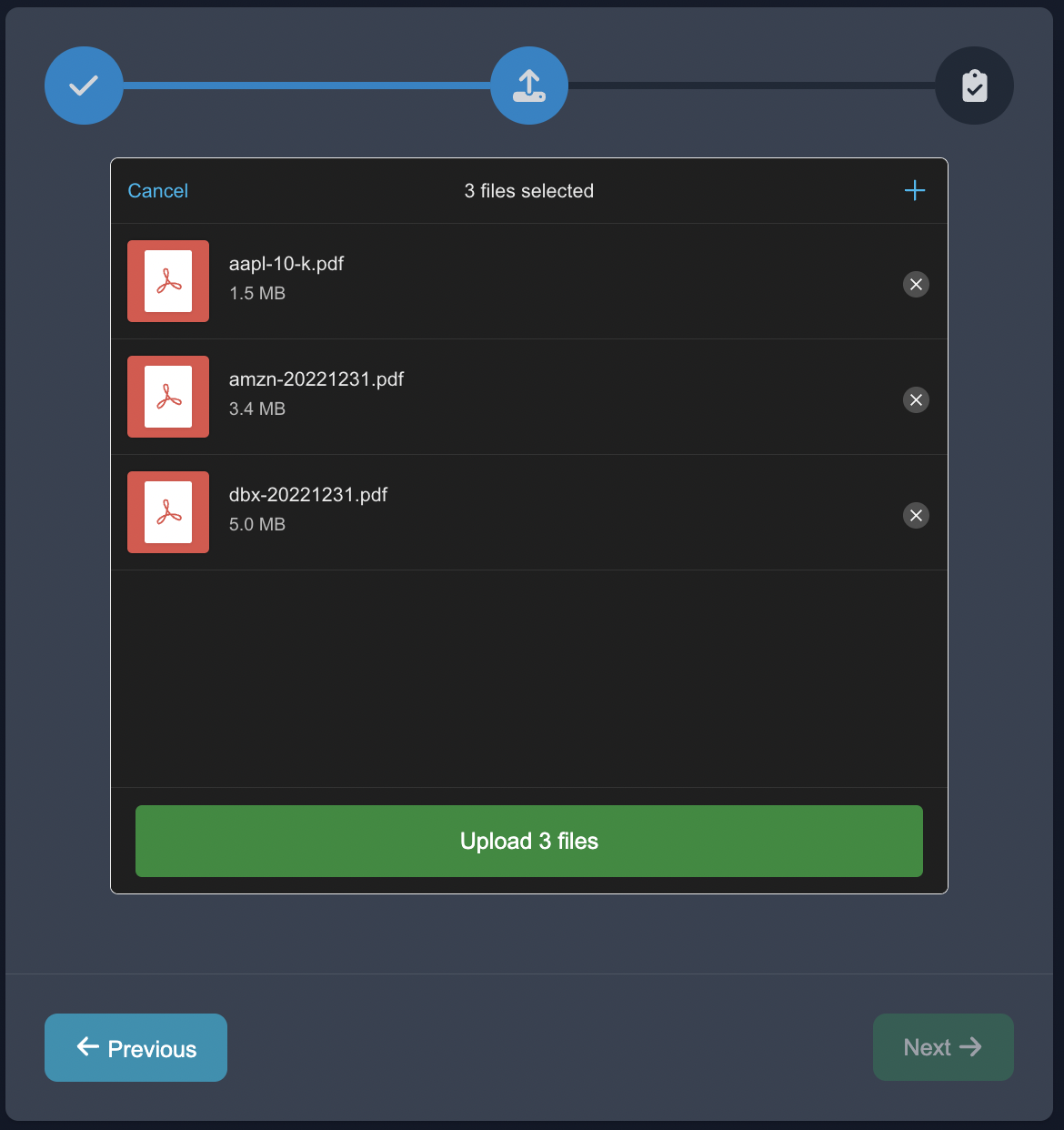
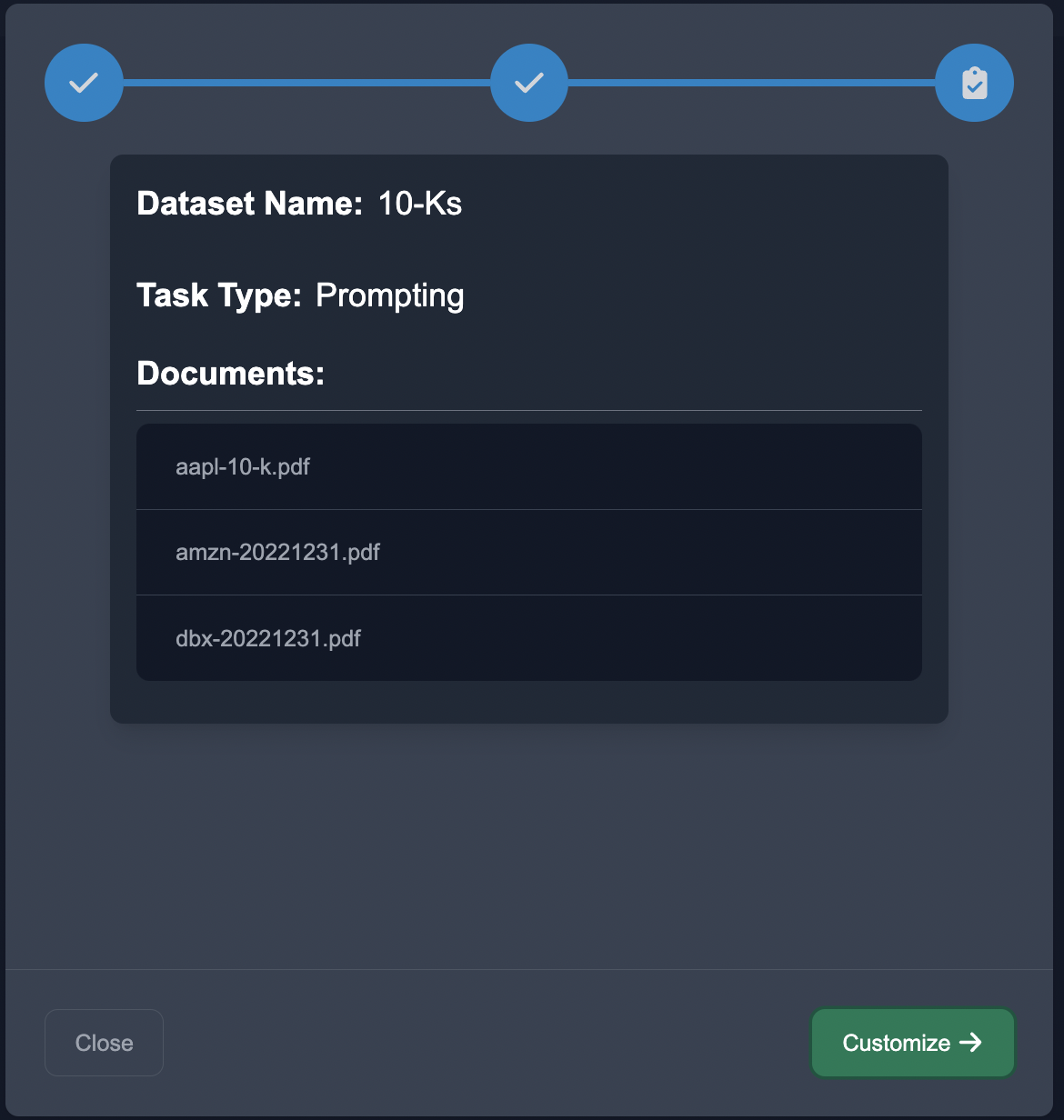
Upload Data
Start by uploading the case studies in the Upload Unstructured format, choose the NLP task of Prompting, and choose the document decomposition.
Customize Questions
Input the relevant questions for the case studies. For example, to extract information from a 10-K report, you could prompt the language model with the following questions:
Prompt: Summarize this document.
Prompt: Is there a risk narrative in this document.
Once you provide a specific prompt or question that instructs the model to summarize the given text, the language model then uses its understanding of language patterns and context to generate a concise and coherent summary.
Annotate
Insert human feedback via inputing the relevant structured and unstructured answers for the questions in the 10-Ks.
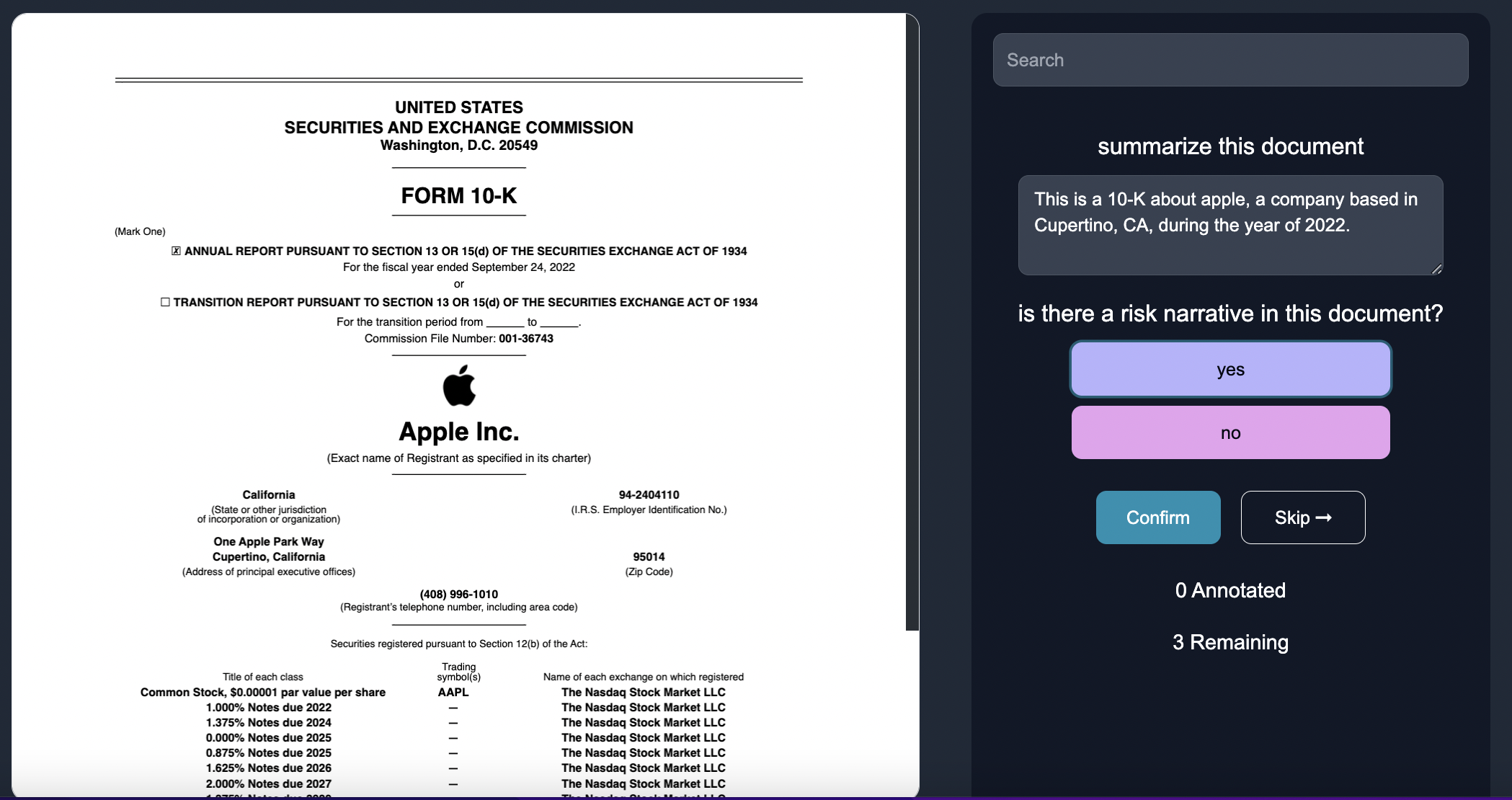
Over time, the model can learn to modify the prompt to be more tailored, such as:
Prompt: can you summarize the financial performance and key highlights of the company mentioned in this 10-K report?
Prompt: Can you identify the specific section, page and citation where the risk narrative occurs, if it is in the 10-K.
Download
We can download the results from the model in a CSV,
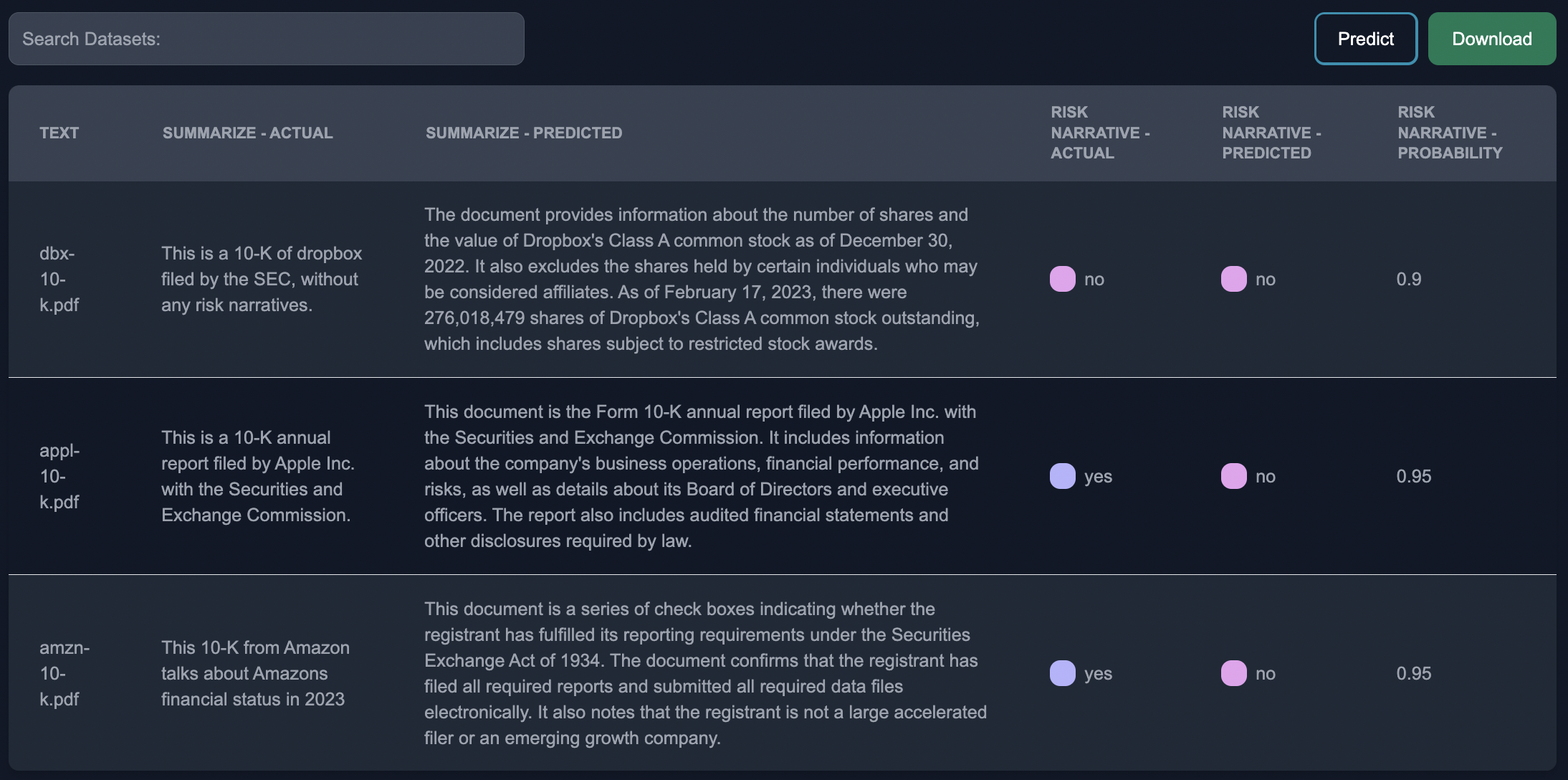
For more details on Anote's work with 10-K's see the 10Ks section of our documentation.
Conclusion
Semi-structured prompting combined with user feedback is a powerful approach for analyzing 10-Ks. Being able to instantaneously obtain critical information a really long document, like a 10-K, can be very useful. For one, we can extract the key information without needing to manually go through the entire document by hand, saving us a lot of time and headache. In addition, because the Large Language Models have been trained on vast amounts of text data, they are able to comprehend the context and extract relevant information to generate accurate summaries, sometimes even better than humans. This saves the human the pain of go through a lot of the jargon to identify the key insights.