Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) can be used to fine-tune financial models, particularly focusing on incorporating human or AI feedback effectively. The process involves using a pre-trained model and enhancing its capabilities through targeted training on a small set of labeled examples.
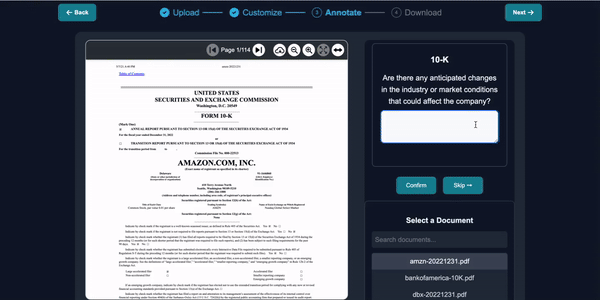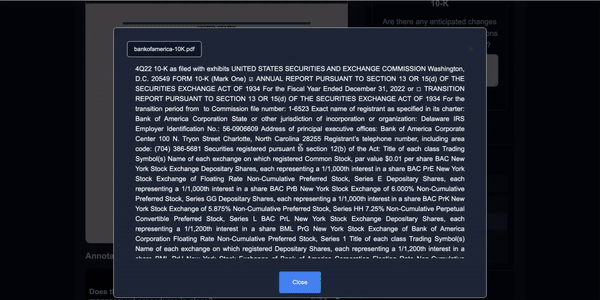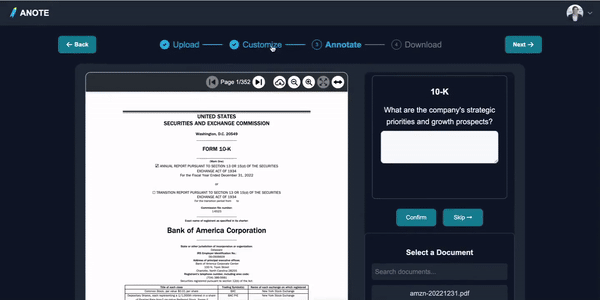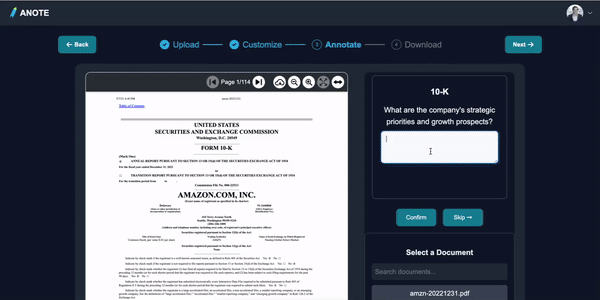
Loading the Pre-trained Model
Start by loading a model that has been previously fine-tuned on financial documents to ensure it has a foundational understanding of financial contexts.
from anoteai import Anote
api_key = 'INSERT_API_KEY_HERE'
Anote = Anote(api_key, isPrivate=False)
fine_tune_model_id = Anote.load_model(
model_name="fine_tuned_mlm_on_10ks",
)['id']
Incremental Training
The RLHF approach involves incrementally training the model by:
- Utilizing labeled examples from a dataset specifically designed for instruction following, such as llmware/rag_instruct_benchmark_tester.
- Conducting training in stages, where each stage refines the model’s understanding based on new sets of feedback.
Reinforcement Learning from Human and AI Feedback
Utilize both human and AI-generated feedback to fine-tune models:
- Human Feedback: Collect demonstrationsof model outputs from human labelers.
- AI Feedback: Use AI to simulate potential improvements for the most effective changes.
If you are interested in RLAIF see our blog post.
Training Process
Fine-tuning is conducted by training a reward model on the dataset where labelers have indicated preferred outputs. This model then serves as a reward function for fine-tuning the primary model using algorithms like Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) or Direct Policy Optimization (DPO).
Using the Fine-Tuned Model
After the model has been enhanced through RLHF, it can be deployed to handle more complex financial queries and provide outputs that align closely with human expectations. By integrating human insights and AI enhancements, financial models can be significantly improved to reduce errors like hallucination and to perform better even with fewer parameters.
# Training Fine Tuned Model using FT-GPT on Financebench
dataset = load_dataset("llmware/rag_instruct_benchmark_tester")
train_df = dataset["train"].to_pandas()
n_increments = 500
for increment in range(n_increments / 5, n_increments, n_increments % 5):
x_train = train_df["question"]
y_train = train_df[["answer", "context"]]
file_paths = list(train_df["doc_link"])
fine_tune_model_id = Anote.train(
x_train_csv=x_train,
y_train_csv=y_train,
initial_model_id=fine_tuned_model_id
model_name="rlhf_" + str(increment) + "_labels",
model_type="llama3",
fine_tuning_type="supervised",
file_paths=file_paths
)['id']
test_df = pd.read_csv("Bizbench.csv")
# Fine Tuned Masked Language Model
for i, row in test_df.iterrows():
row["rlhf_" + str(increment) + "_answer"], \
row["rlhf_" + str(increment) + "_chunk"] = Anote.predict(
model_name="rlhf_" + str(increment) + "_labels",
model_id=fine_tuned_model_id,
question_text=row["question"],
context_text=row["context"]
)
test_df[["id", "rlhf_" + str(increment) + "_answer"]].to_csv("rlhf_" + str(increment) + "_submission.csv")
Additional Resources
- Training Language Models to Follow Instructions with Human Feedback talks about OpenAI's research on RLHF and its applications to fine-tuning language models like GPT-3.
- Model Card for Instruction Following Model shares techniques for training smaller models to outperform larger ones through effective feedback utilization.