Evaluating Q&A Models
Evaluation metrics are important to measure how each fine tuned model performs versus raw traditional models such as GPT4 or Llama3. We use evaluation metrics understand and quantify performance of the fine tuned LLMs, to ensure they perform accurately.
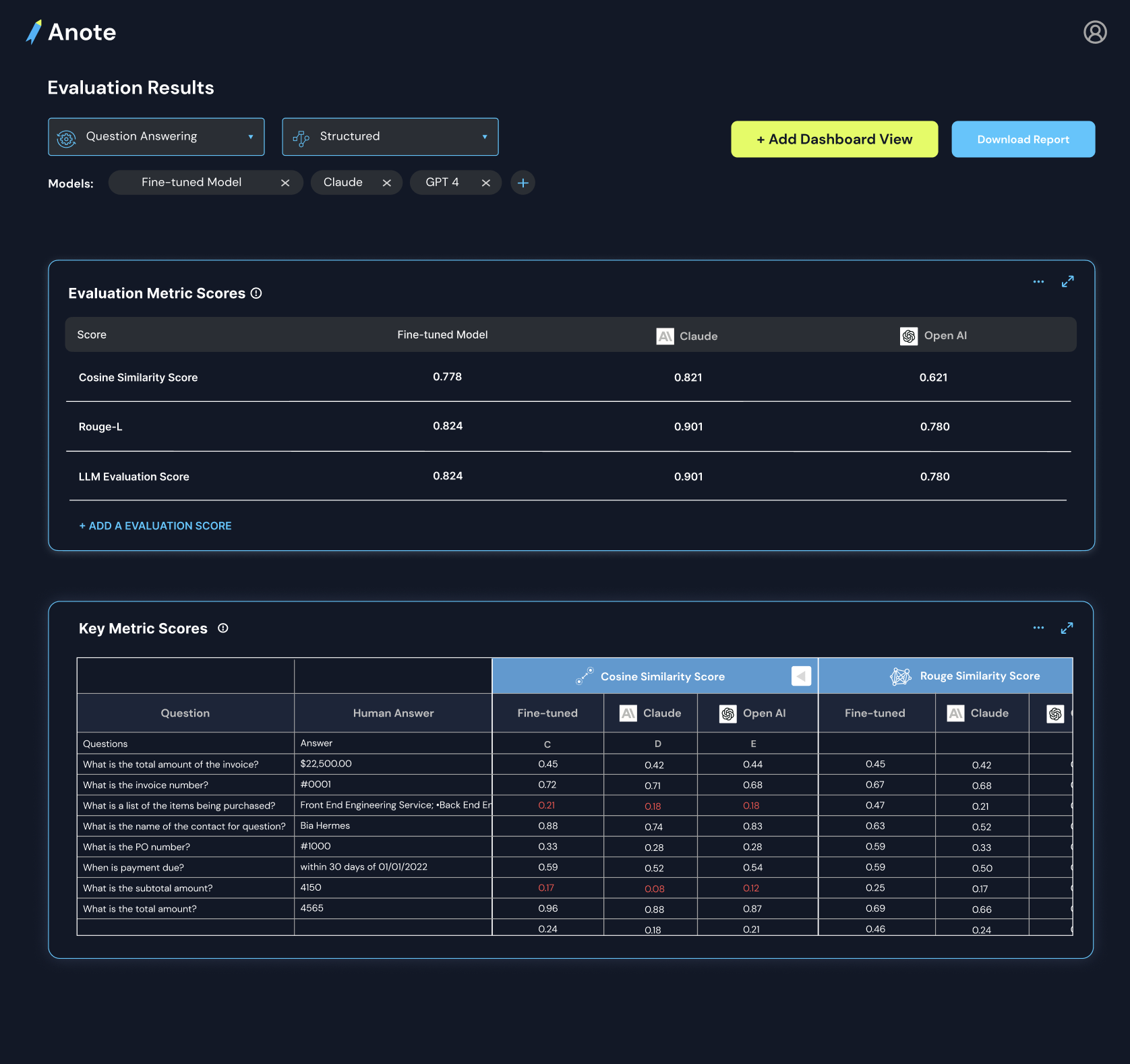
Structured vs. Unstructured Evaluation
When it comes to evaluating question and answering models on financial documents, the two main components are evaluating the model’s ability to retrieve context as well as its ability to answer questions based on the context. Ideally, we have access to ground truth context and answers developed by human financial analysts for structured evaluation.
| Question | Human Answer | Human Chunk | Claude Model Answer | Claude Model Chunk | Llama Model Answer | Llama Model Chunk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| What is the total amount of the invoice? | $22,500.00 | Total Amount $22,500.00 | $22,500.00 | total amount $22,500.00 | $22,500.00 | about Total Amount $22,500.00 |
| What is the invoice number? | #0001 | INVOICE # 0001 | #0001 | about INVOICE # 0001 | #0001 | INVOICE # 0001 |
| What is a list of the items being purchased? | •Front End Engineering Service; •Back End Engineering Service; •Quality Assurance Manager | Front End Engineering Service $5000.00 Back End Engineering Service $7500.00 Quality Assurance Manager | •front end engineering service; •back end engineering service; •quality assurance manager | FRONT END ENGINEERING SERVICE $5000.00 BACK END ENGINEERING SERVICE $7500.00 QUALITY ASSURANCE MANAGER | •front end engineering service; •back end engineering service; •quality assurance manager | about Front End Engineering Service $5000.00 Back End Engineering Service $7500.00 Quality Assurance Manager |
| What is the name of the contact for question? | Bia Hermes | contact Bia Hermes | bia hermes | about contact Bia Hermes | Bia Hermes | contact bia hermes |
| What is the PO number? | #1000 | P.O. # 1000 | about #1000 | P.O. # 1000 | #1000 | p.o. # 1000 |
| When is payment due? | within 30 days of 01/01/2022 | Payment is due within 30 days | WITHIN 30 DAYS OF 01/01/2022 | PAYMENT IS DUE WITHIN 30 DAYS | WITHIN 30 DAYS OF 01/01/2022 | Payment is due within 30 days |
Notice how there is human labeled answers and chunks above, so we can compare each model's answers and chunks from Claude and Llama3 to the human labeled answer (which we take as ground truth). However, in scenarios where we do not have access to this ground truth data, we need metrics that inform us about the quality of the chunk and answer from the model, hence unstructured evaluation .
| Question | Claude Model Answer | Claude Model Chunk | Llama Model Answer | Llama Model Chunk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| What is the total amount of the invoice? | $22,500.00 | total amount $22,500.00 | $22,500.00 | about Total Amount $22,500.00 |
| What is the invoice number? | #0001 | about INVOICE # 0001 | #0001 | INVOICE # 0001 |
| What is a list of the items being purchased? | •front end engineering service; •back end engineering service; •quality assurance manager | FRONT END ENGINEERING SERVICE $5000.00 BACK END ENGINEERING SERVICE $7500.00 QUALITY ASSURANCE MANAGER | •front end engineering service; •back end engineering service; •quality assurance manager | about Front End Engineering Service $5000.00 Back End Engineering Service $7500.00 Quality Assurance Manager |
| What is the name of the contact for question? | bia hermes | about contact Bia Hermes | Bia Hermes | contact bia hermes |
| What is the PO number? | about #1000 | P.O. # 1000 | #1000 | p.o. # 1000 |
| When is payment due? | WITHIN 30 DAYS OF 01/01/2022 | PAYMENT IS DUE WITHIN 30 DAYS | WITHIN 30 DAYS OF 01/01/2022 | Payment is due within 30 days |
Structured Evaluation Answer Accuracy
Answer accuracy takes in the model answer and ground truth answer to evaluate whether or not the model is correct or not. For questions asking for a particular numerical metric, we can use a binary evaluation via regex expressions to say whether it is correct or not. However for open ended, explanation based questions in natural language, it can be more complicated, so we can utilize the following metrics for evaluating answer accuracy:
| Metrics | Description | Example of Calculation |
|---|---|---|
LLM eval |
This metric serves as a substitute for human evaluation, where we can prompt a model like GPT-4 to see if two answers have the same semantic meaning, and prompt it to assign a specific score | Use GPT-4 to evaluate the semantic similarity between "The sky is clear" and "It's a cloudless day" and assign a score. |
Cosine Similarity |
This is a more automated way of comparing semantic meaning, however relies on both answers being extremely similar in order to have a high score | Calculate the cosine similarity of the TF-IDF vectors for the sentences "I enjoy reading books" and "Reading books is enjoyable". |
Rouge-L Score |
This metric is based on the longest common subsequence (LCS) between our model output and reference | Calculate the Rouge-L score by finding the LCS of "The cat is sleeping on the mat" and "A cat sleeps on a mat". |
Bleu Score |
This metric compares how similar two texts are as a number between 0 and 1. Generally a score of at least 0.6 means that two texts are similar enough to mean the same thing. | Calculate the Bleu Score for machine translated text compared to a human reference translation to assess quality. |
However, for the use case of answering questions on many long financial documents, oftentimes the answers to questions can be wrong or incorrect. Sometimes it is due to more answers from the model, but more often than not it is due to the model thinking the answer is in the wrong part of the document. Because of this, retrieval systems such as RAG focus on identifying the right source / chunk of text to better inform the answer, that way the answer is coming from the right section in the document.
Retrieval Accuracy:
It is important to evaluate retrieval accuracy because if the chunk in the document that the model sources is incorrect, the answer to the question from the model is most likely going to be wrong. Retrieval accuracy metric takes into account the context in addition to the answer as a way to evaluate how well the pipeline can retrieve the correct section. With access to the ground truth context, we can evaluate document level, page level and paragraph level, and multi-chunk level accuracies for retrieval.
| Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
document level |
This metric checks if retrieved chunk is on the same document in the document as the actual chunk |
page level |
This metric checks if retrieved chunk is on the same page in the document as the actual chunk |
paragraph level |
This metric checks if retrieved chunk is on the same paragraph in the document as the actual chunk |
multi-chunk level |
This metric checks if multiple retrieved chunk are found in the same place in the document as the actual chunks |
Multi-chunk level accuracies is still a work in progress, and is very important for cases where answers to questions come from multiple chunks / pages / documents, where each chunk has contains an important part of information required for the answer. On the retrieval side, this is a limitation with RAG based systems that only find the top most similar chunk (where the similar chunk might not be the most relevant chunk).
Unstructured Evaluation Metrics
Without access to ground truth answers, most of the evaluation metrics will be based on whether or not the model answer is grounded in the context retrieved. These metrics are from the RAGAS evaluation framework.
| Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
Faithfulness |
This metrics evaluates whether the answer is supported by the given context, and penalizes the model if it hallucinated information not supported by the text. |
Answer Relevance |
This metric evaluates whether or not the answer actually addresses the question. It does not account for accuracy, but penalizes for incomplete/redundant answers |
These are the metrics currently supported from within our public chatbot SDK, as when you use a chatbot such as Private Chatbot, Perplexity, GPT, Bard or Claude, there is no source of ground truth for model answers to be compared against.
Identifying Anomalies and Measuring Trustworthiness
Within the Anote documentation, we have resources in regards to identifying anomalies in answers to questions. We leverage cosine similarity to measure trustworthiness, to ensure the models output reliable results, and flag the rows where model answers appear to be incorrect.
Aggregate Metrics
In addition to understanding how each specific row metric performed for each specific question, answer, chunk, it's important to have aggregate metrics across the entire testing dataset. Aggregate metrics are important for benchmarking different fine tuned models across an entire testing data corpus. This could look something like the following.
| Aggregate Evaluation Metrics | Claude | Open AI | RLHF Model 10 Labels | Unsupervised FT Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cosine Similarity Score |
0.778 | 0.821 | 0.621 | .580 |
Rouge-L Score |
0.824 | 0.901 | 0.780 | .618 |
LLM Evaluation Score |
0.802 | 0.821 | 0.650 | .838 |
What is important to note is that model performance is determined by the evaluation metrics specified, so the user should be able to add metrics that they care about for their specific domain to measure model performance.