Summarization
Summarizing long documents can be a time-consuming and challenging task. One approach to simplify the process is by leveraging the power of large language models to generate summaries based on given prompts.
Example: Semi-Structured Summarization for Resumes
Analyzing resumes is a nuanced task that demands understanding of various components like education, skills, experience, and achievements. Employing the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT with summarization and semi-structured prompting can significantly boost the effectiveness and precision of resume analysis. Here's how semi-structured summarization works in the context of a resume analysis on Anote, where we ask questions on resumes, and use human input to refine the predictions of LLMs.
For example of how this can be applicable, to summarize a resume, you could provide a prompt like: Summarize this resume in 2 sentences.
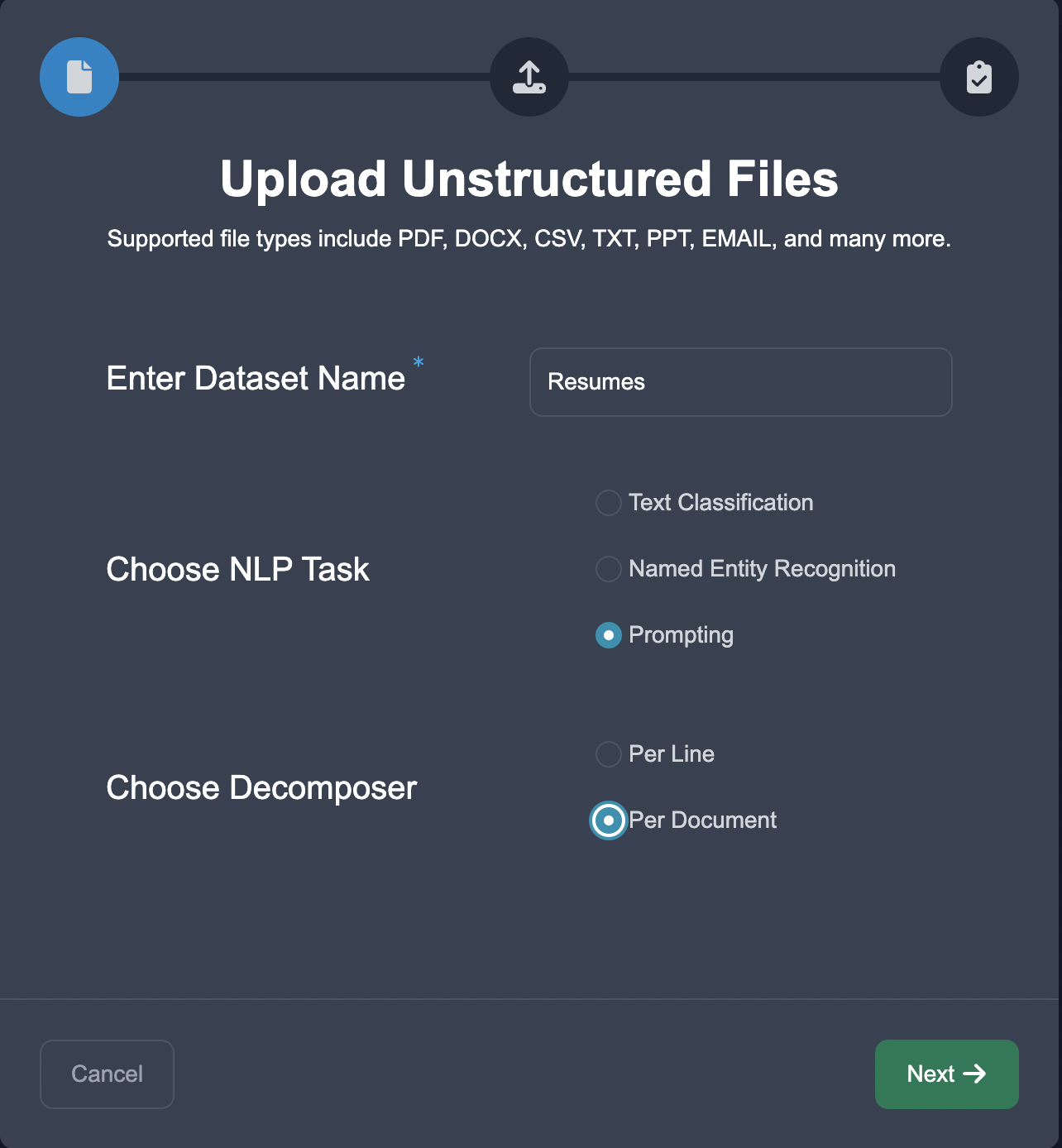
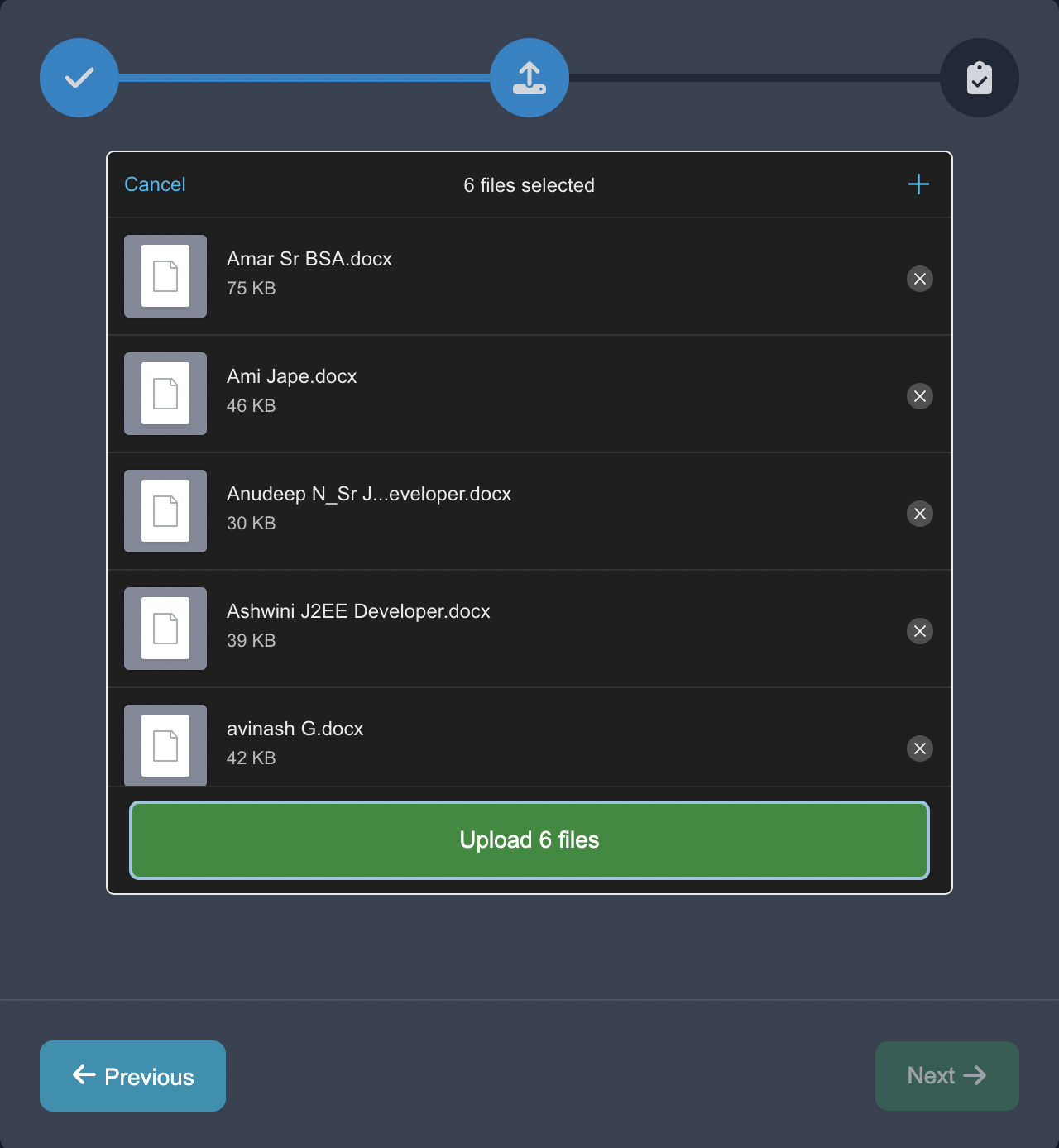
Upload Data
Start by uploading the case studies in the Upload Unstructured format, choose the NLP task of Prompting, and choose the document decomposition.
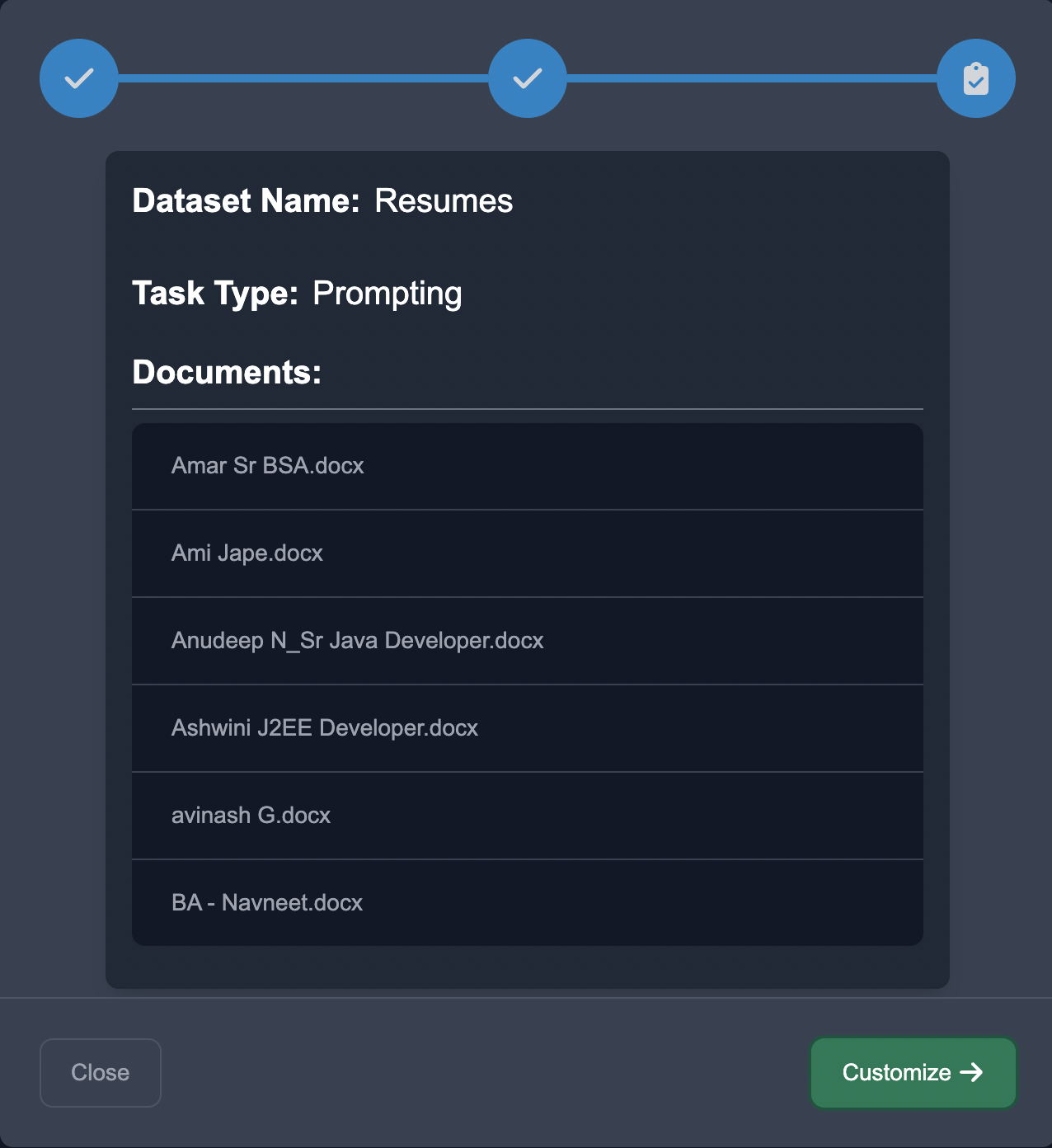
Customize Questions
Input the relevant questions for the case studies. For example, to extract information from a resume, you could prompt the language model with the following questions:
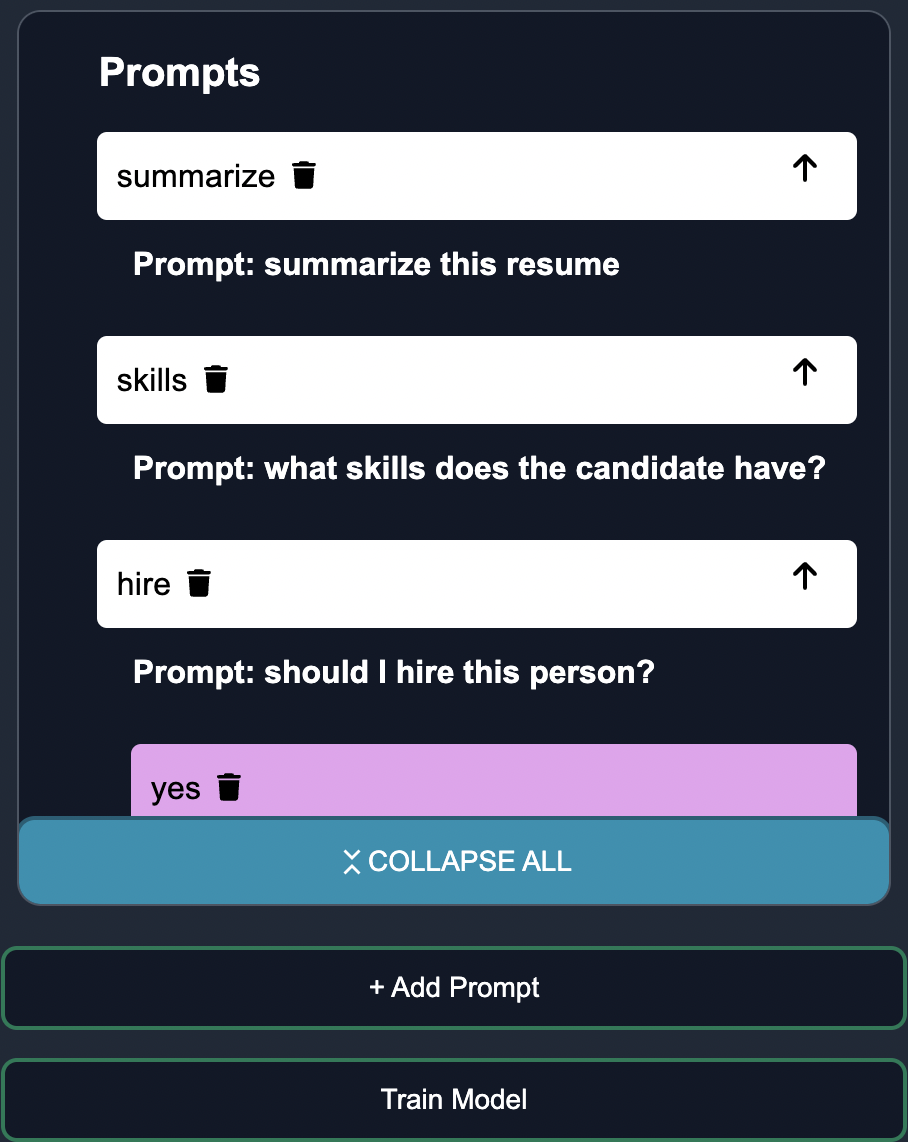
If you would prefer a more detailed response, you can always refine your prompt in the customize tab to something like the following prompt:
Prompt: Please generate a summary highlighting the candidate's key skills, experiences, and achievements.
Annotate
The LLM will generate a response, given the question you ask and data you upload. For instance, your LLM might generate the following summary as output.
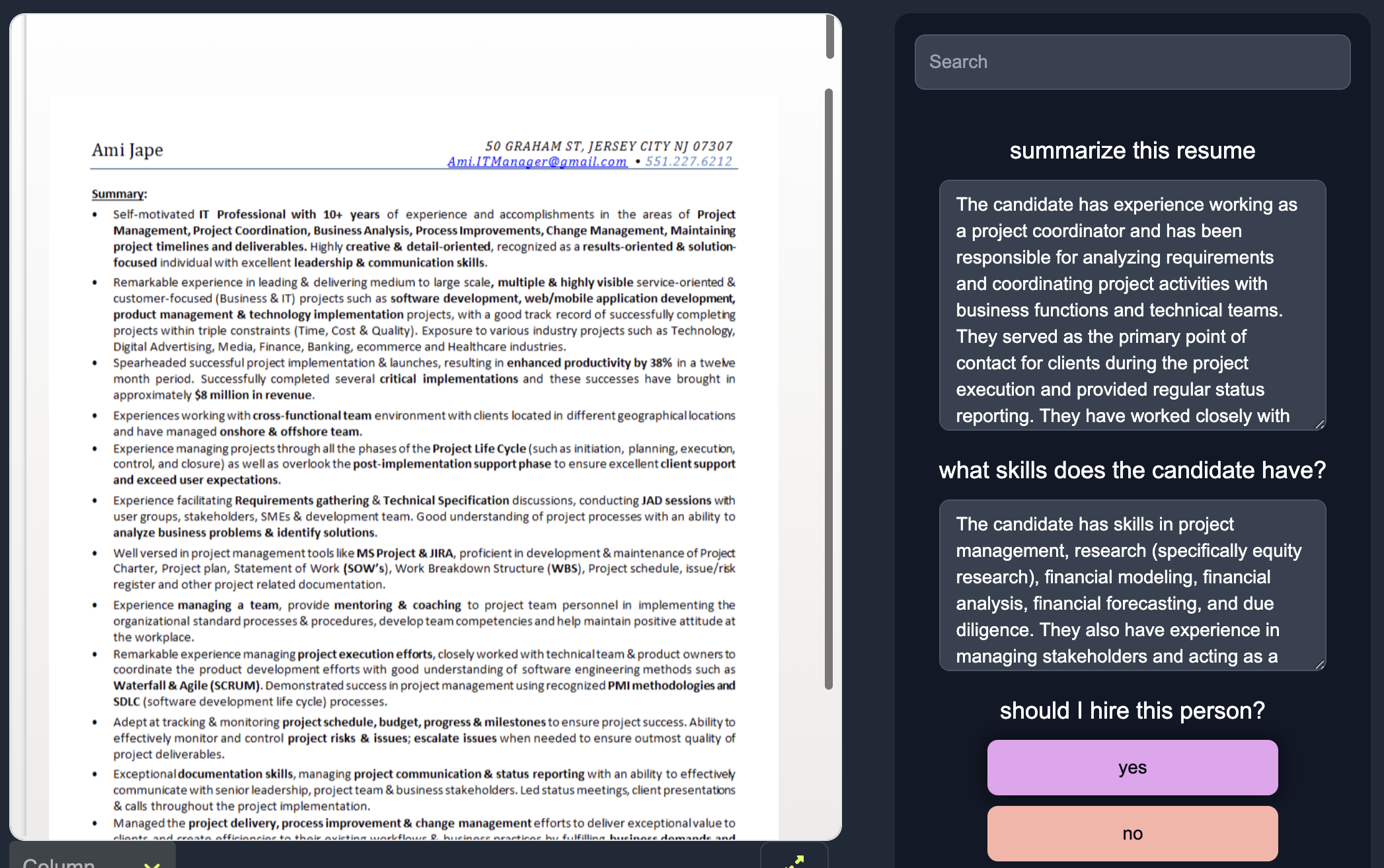
Generated Summary: John Doe is a Software Engineer with expertise in Python, Java, and C++. He has experience in developing web applications using Django and has strong problem-solving and analytical skills. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science and has received recognition for his exceptional performance and dedication at ABC Tech. Additionally, he has published a research paper on machine learning in a reputable conference.
However, the generated summary might be different than the actual summary that we would want, so we may want to update the summary by hand to the following output.
Actual Summary: John Doe is an experienced Software Engineer proficient in Python, Java, and C++. He has developed web applications using Django, collaborated with cross-functional teams.
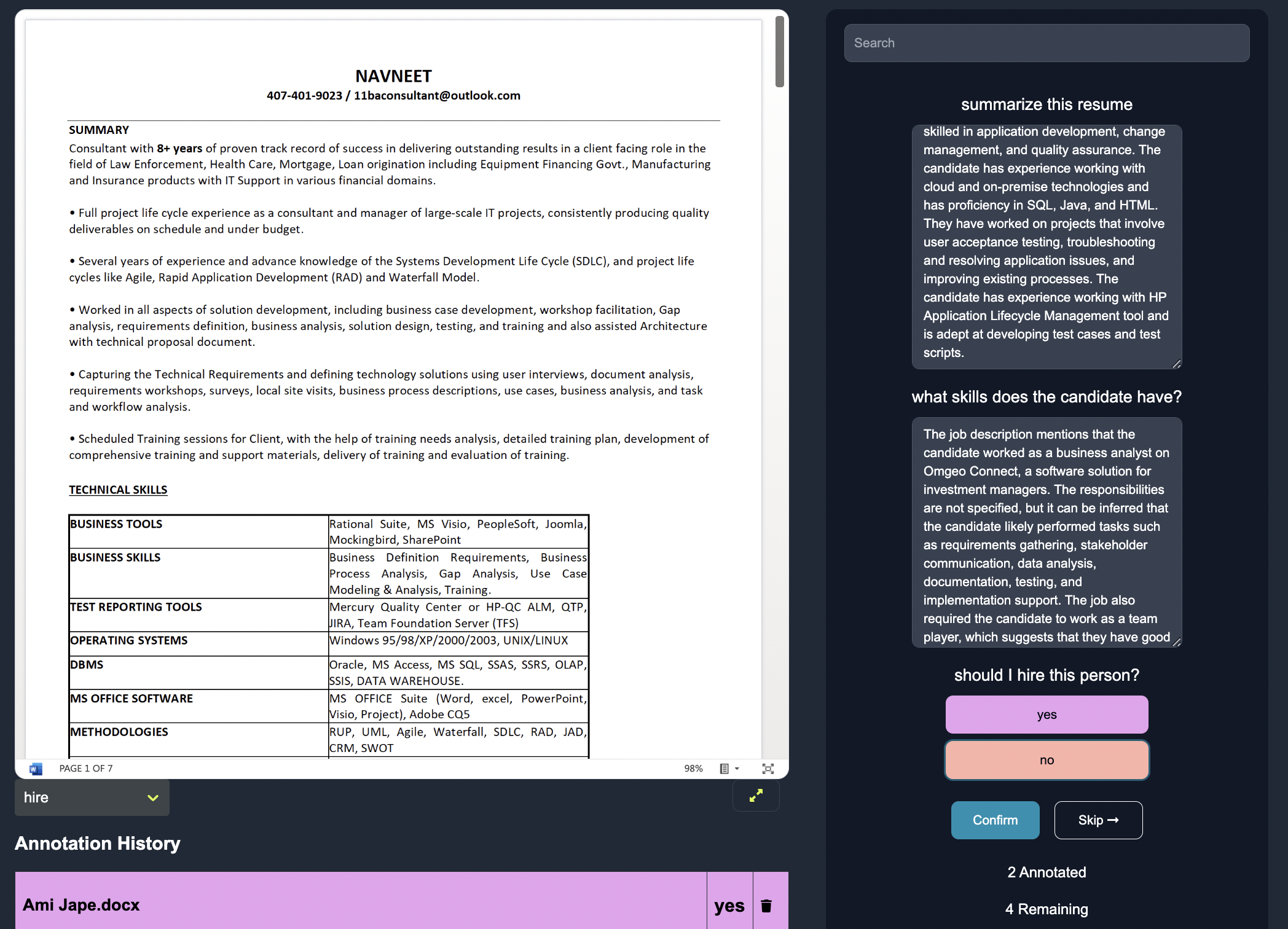
You can imagine that as the amount of documents becomes relatively large, on the order of millions of documents, updating the summaries for each document by hand could become incredibly tedious and time consuming. On Anote, we can learn from human feedback to predict better summaries with just a few human interventions.
User Feedback - The Trick to Finding Better Summaries
User feedback plays a crucial role in refining the summarization process. Here is a high level guide on how we incorporate human feedback to find the ideal summaries across millions of documents with just a few interventions
1. Embedding Space Comparison: By representing the generated summary and the user's summary in the embedding space, we can measure the similarity or dissimilarity between them. This comparison helps us quantify the differences and identify areas where the generated summary can be improved.
2. Reprompting and Retraining: Based on the differences observed in the embedding space, we can re-prompt the language model with more specific or targeted prompts to guide the summarization process towards the desired output. Additionally, we can incorporate the user's own summary as training data to fine-tune the model and improve its performance over time.
3. Iterative Refinement: Through an iterative process of gathering user feedback, analyzing differences, re-prompting, and retraining, we can continually refine the summarization model. This feedback loop allows us to adapt the language model to specific document types, address domain-related nuances, and produce more accurate and relevant summaries based on human preferences.
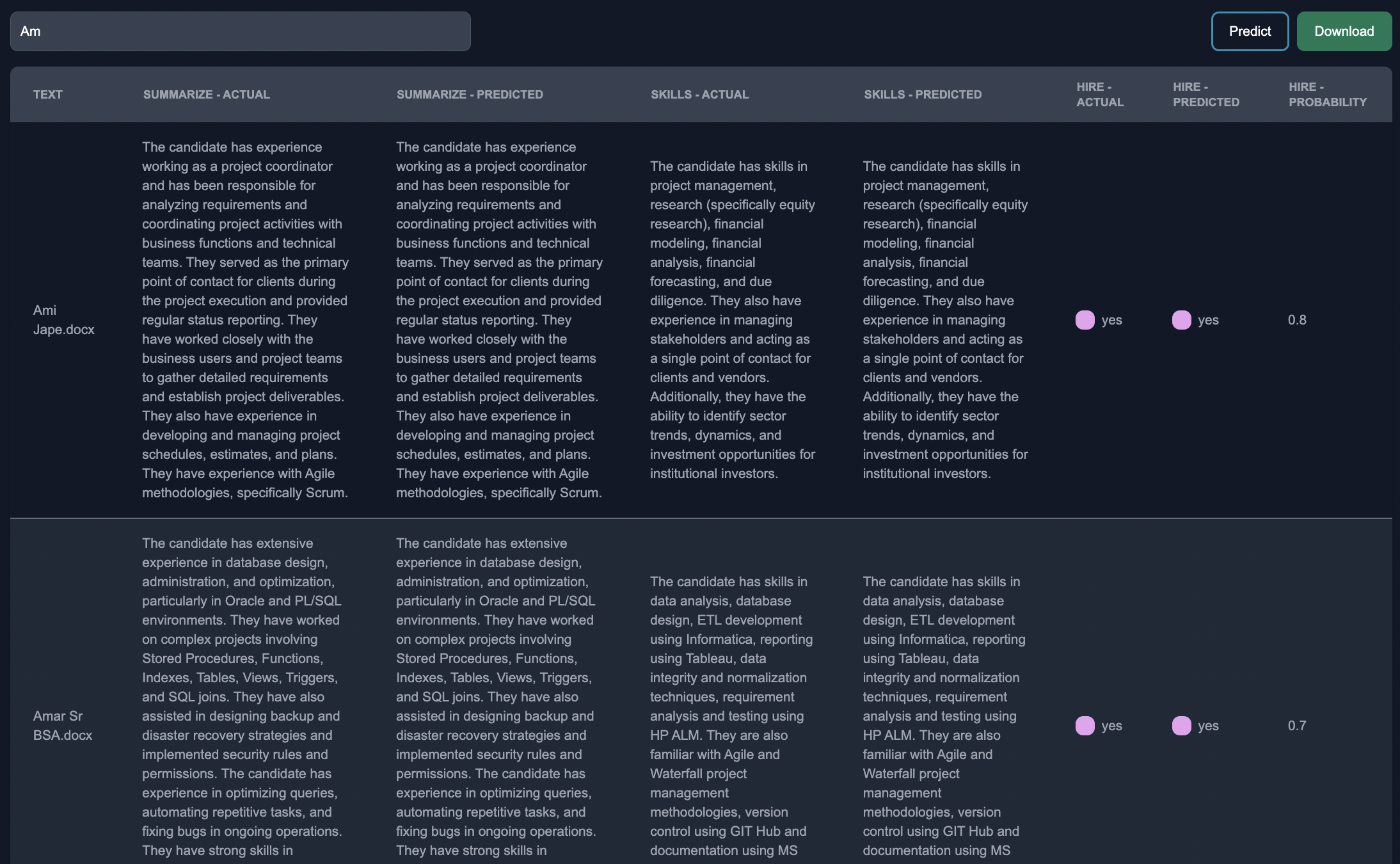
Download Results
In the table below, you can see the model response, and the human feedback. Depending on if the output of the model is structured (categorical) or unstructured (freeform), we leverage unique approaches to learn from the actual human feedback to adjust the model predictions to make them more tailored to the end user.
Impact on Businesses
Companies have an abundance of resumes on file but lack the time to thoroughly read each one. With Anote, recruiters, who used to manually reviewed 1,000 candidate resumes that matched the keywords "Data Analyst" and "Python", can obtain the critical information they need in a fraction of the time.
Conclusion
Summarizing long documents using language models provides an efficient and automated approach. By leveraging user feedback and adjusting the summarization process based on differences observed in the embedding space, we can continuously improve the quality and accuracy of the generated summaries. After a few examples of human feedback, the summaries are able to become domain specific, which can save people a lot of time going through vast quantities of documents and data.