What is Artificial Intelligence?
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
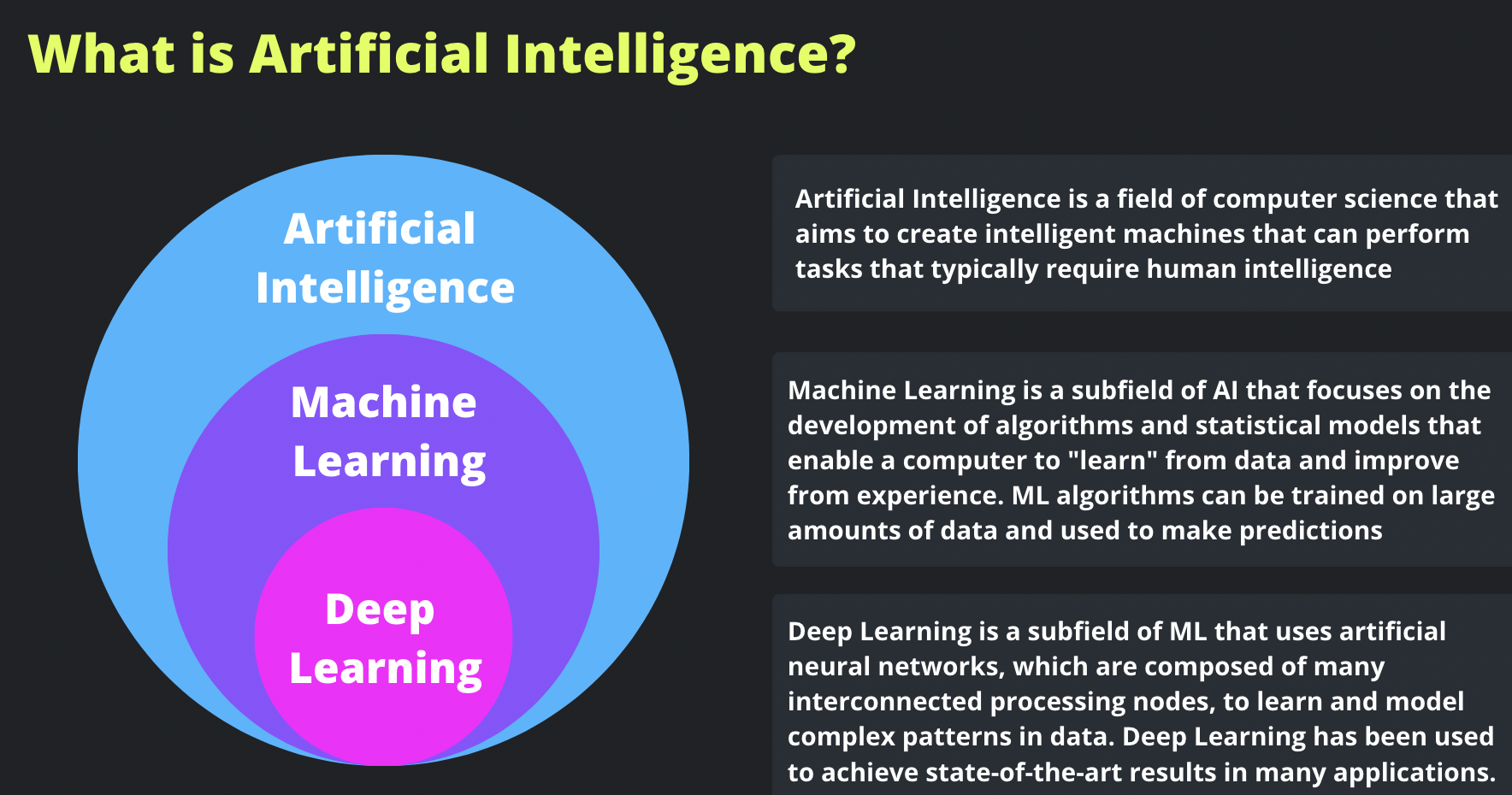
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a fascinating field of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. It encompasses a wide range of techniques and approaches to simulate human-like behavior and decision-making processes.
Machine Learning (ML), a subfield of AI, focuses on developing algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to "learn" from data and improve their performance through experience. ML algorithms can analyze and extract patterns from large amounts of data, allowing them to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed.
Deep Learning, a subfield of ML, utilizes artificial neural networks that are composed of interconnected processing nodes. These networks are designed to mimic the structure and functioning of the human brain. Deep Learning models excel at learning and modeling complex patterns and relationships in data, enabling them to achieve state-of-the-art results in various domains.
Advent of Deep Learning
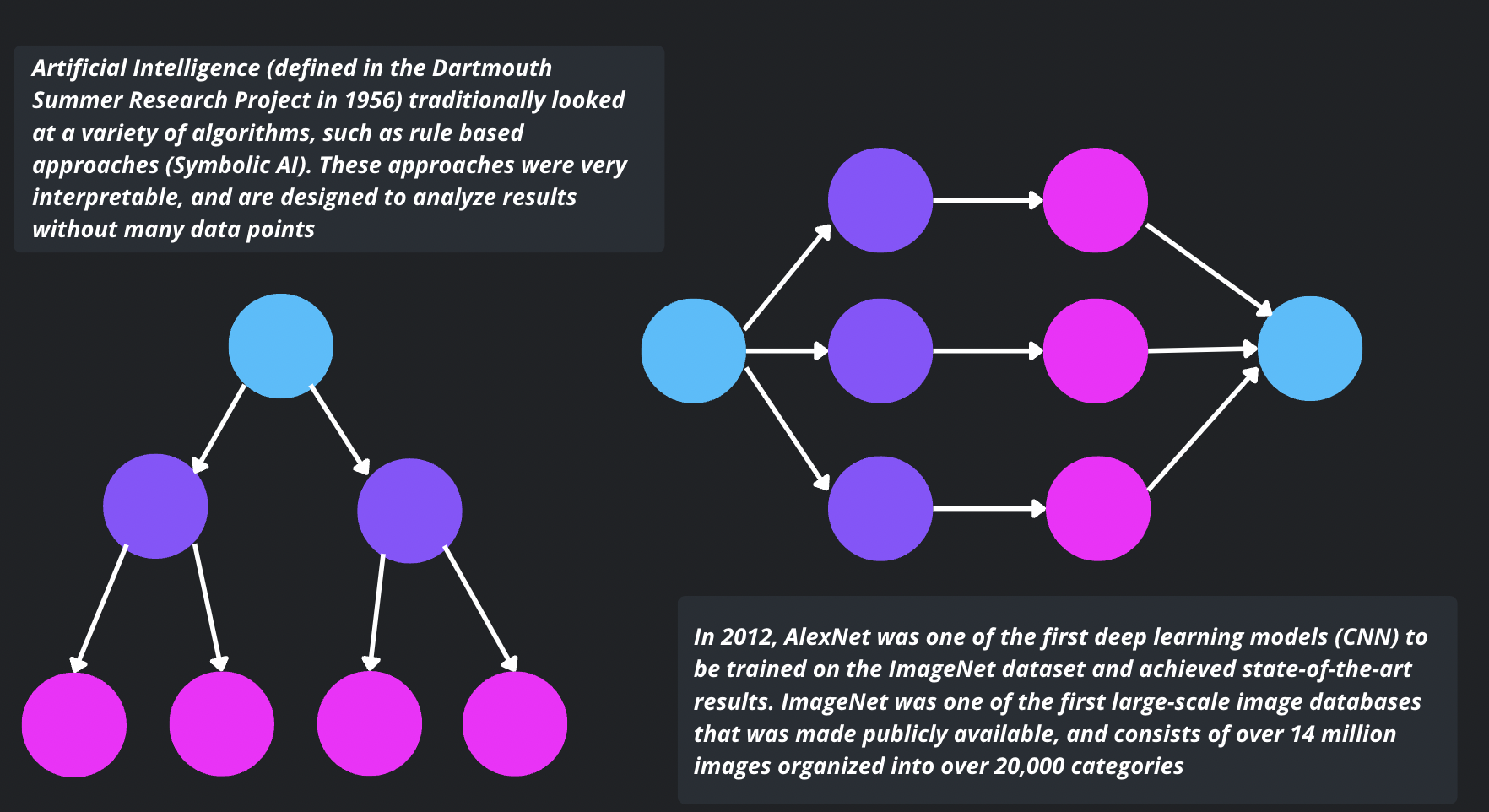
Artificial Intelligence (defined in the Dartmouth Summer Research Project in 1956) traditionally looked at a variety of algorithms, such as rule based approaches (Symbolic AI). These approaches were very interpretable, and are designed to analyze results without many data points.
In 2012, AlexNet was one of the first deep learning models (CNN) to be trained on the ImageNet dataset and achieved state-of-the-art results. ImageNet was one of the first large-scale image databases that was made publicly available, and consists of over 14 million images organized into over 20,000 categories.
In recent years, Deep Learning has revolutionized many fields, including computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, and recommendation systems. Its ability to automatically learn hierarchical representations from raw data has contributed to significant advancements in AI applications.
Summary
Modern machine learning, particularly deep learning, relies heavily on labeled data for training accurate models. Labeled data serves as the foundation for supervised learning, enabling algorithms to learn patterns and make predictions based on the provided labels. By leveraging the power of ML and Deep Learning, researchers and practitioners continue to push the boundaries of AI, unlocking new possibilities and applications across various industries.